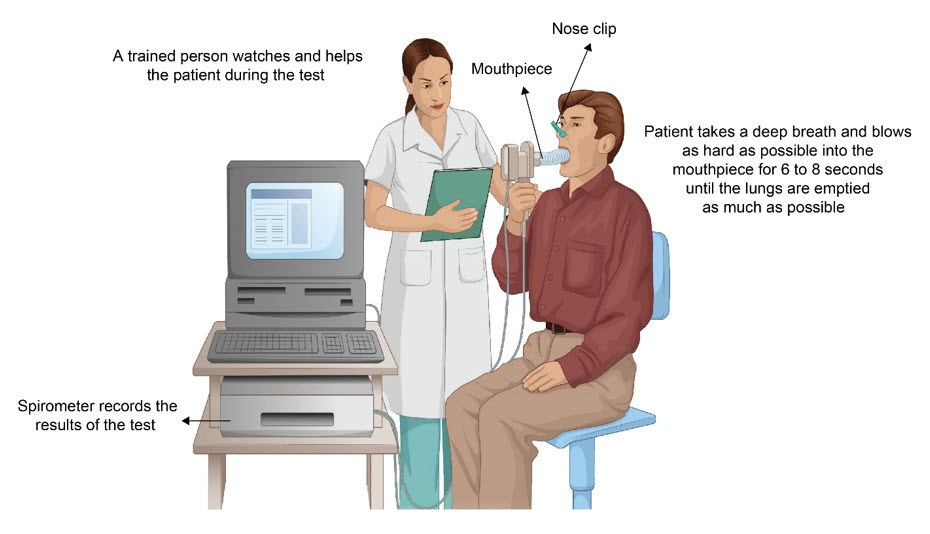
Pulmonary function tests are a series of non-invasive tests that assess breathing and how well the lungs are working. Pulmonary function testing generally includes measurements of airflow, lung volume, and diffusion capacity, or the ability of the lungs to move oxygen from the air into the bloodstream and to move carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the lungs.
Read More
Pulmonary function tests are a series of non-invasive tests that assess breathing and how well the lungs are working. Pulmonary function testing generally includes measurements of airflow, lung volume, and diffusion capacity, or the ability of the lungs to move oxygen from the air into the bloodstream and to move carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the lungs.
Read More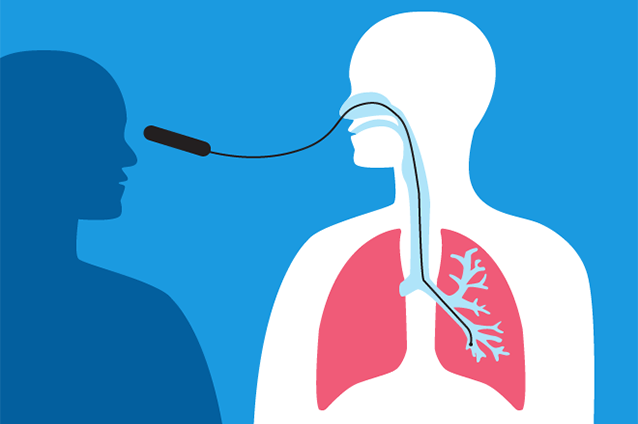
Bronchoscopy is a test that allows a doctor to view the airways (bronchi) with the use of a thin, lighted tube containing a camera. The tube used in bronchoscopy may be flexible or rigid. The flexible scope is most often used. The rigid scope is a straight tube and is only used to view the larger airways. Bronchoscopy, also called fiberoptic bronchoscopy, is used to diagnose and sometimes treat lung conditions.
Read More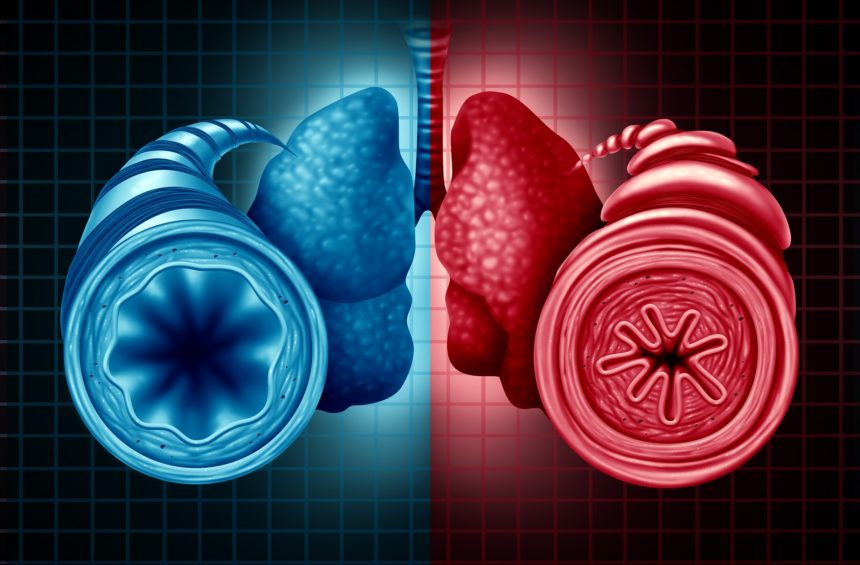
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production and wheezing. It's caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke. People with COPD are at increased risk of developing heart disease, lung cancer and a variety of other conditions.
Read More
Interstitial lung disease describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream. Interstitial lung disease can be caused by long-term exposure to hazardous materials, such as asbestos. Lung transplant is an option for some people who have interstitial lung disease.
Read More
Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea causes daytime sleepiness, worsening of hypertension, diabetes and cardio-vascular complications. Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea have an accident rate of seven times that of normal people. Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts. If you snore loudly and feel tired even after a full night's sleep, you might have sleep apnea.
Read More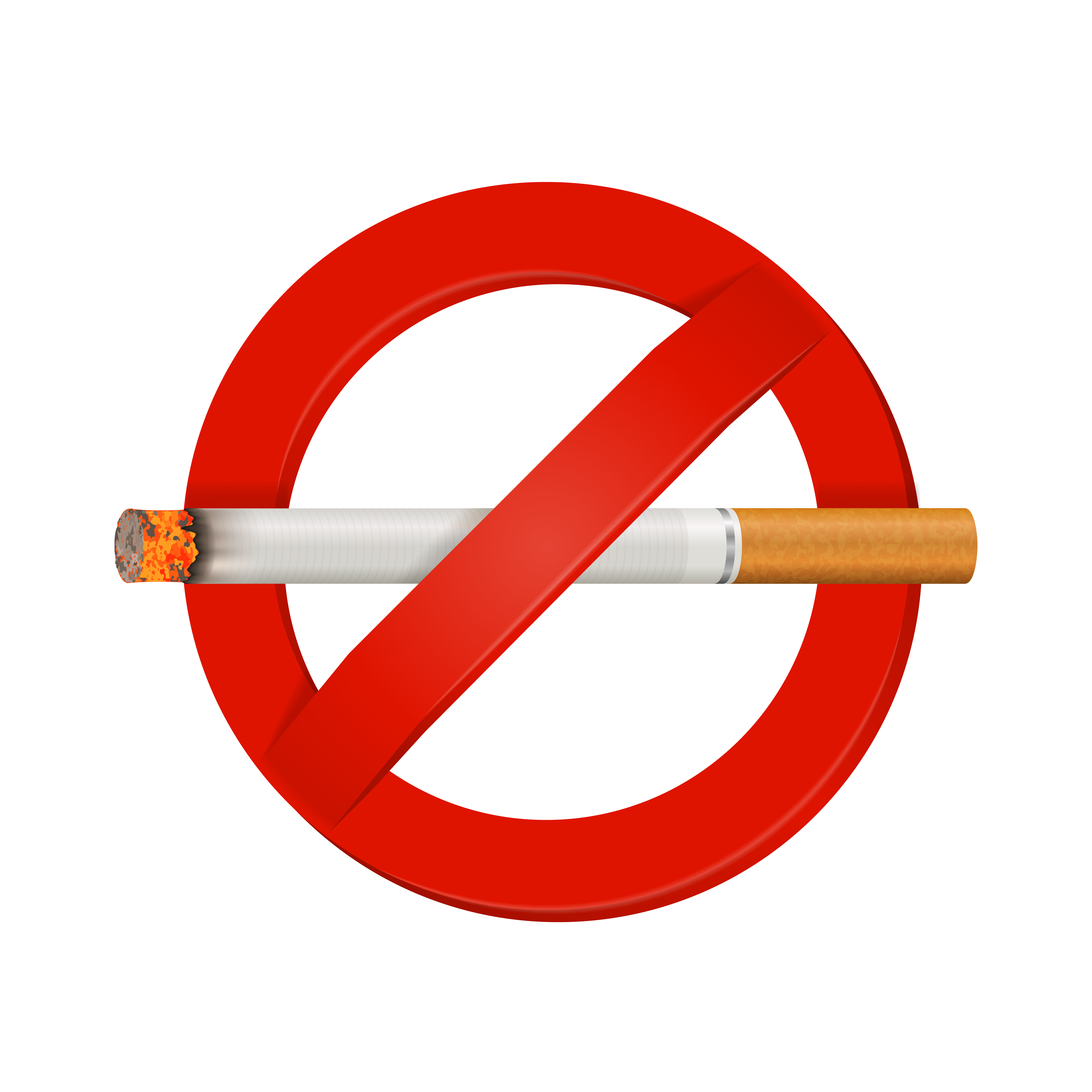
Smoking cessation (also known as quitting smoking or simply quitting) is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive. Nicotine withdrawal makes the process of quitting often very prolonged and difficult. Smoking is the leading preventable cause of death worldwide. Tobacco cessation significantly reduces the risk of dying from tobacco-related diseases.
Read More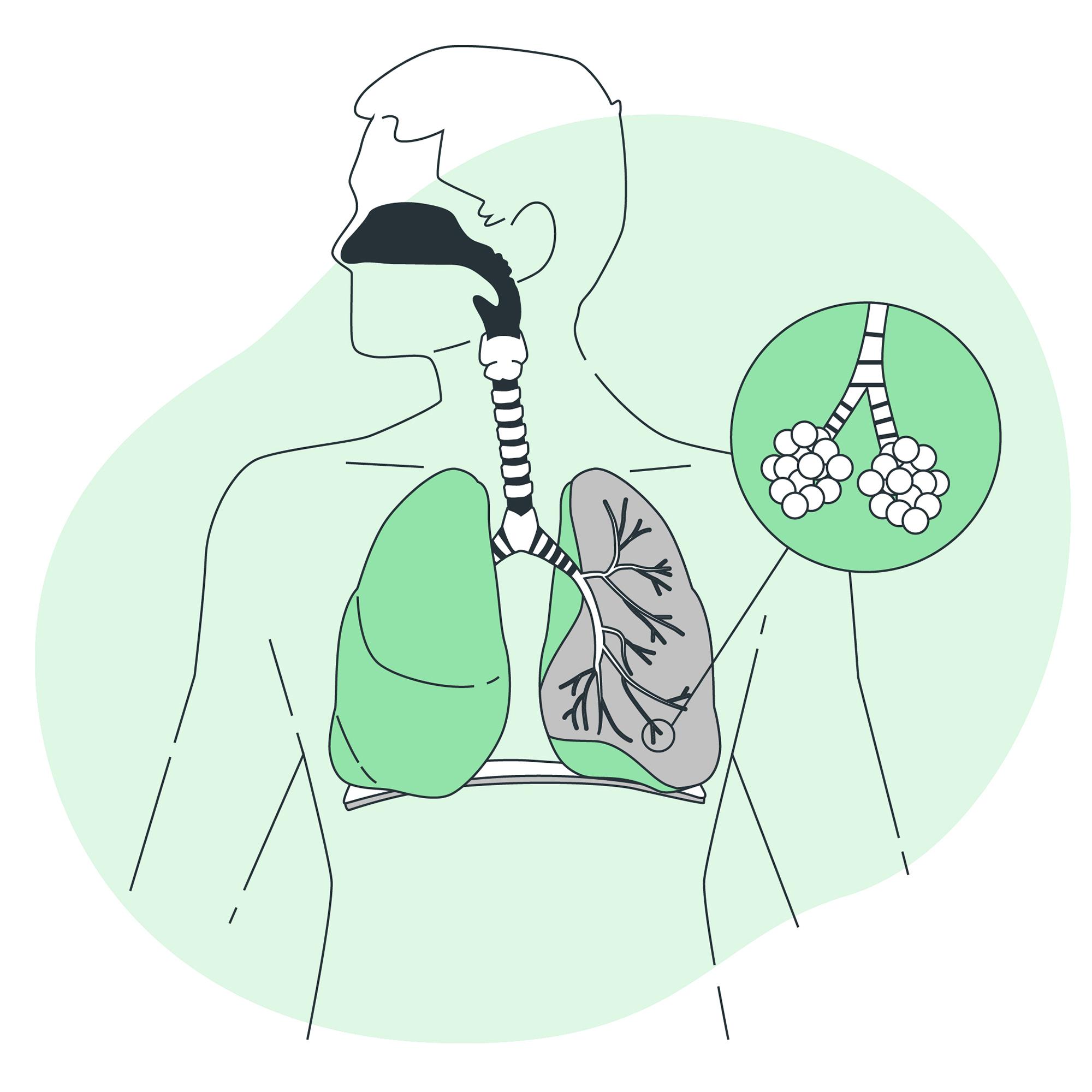
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially serious infectious disease that mainly affects your lungs. The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from one person to another through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes. Many strains of tuberculosis resist the drugs most used to treat the disease. People with active tuberculosis must take several types of medications for many months to eradicate the infection and prevent development of antibiotic resistance.
Read More
A chronic cough is a cough that lasts eight weeks or longer in adults, or four weeks in children. A chronic cough is more than just an annoyance. A chronic cough can interrupt your sleep and leave you feeling exhausted. Severe cases of chronic cough can cause vomiting, lightheadedness and even rib fractures. While it can sometimes be difficult to pinpoint the problem that's triggering a chronic cough, the most common causes are tobacco use, postnasal drip, asthma and acid reflux.
Read More